LoRa makes the industrial IoT more accessible. So what is it and what does it mean? We have gathered frequently asked questions and answers here. Do you have more questions? Please contact Us!
Why wireless traffic system for industrial IoT?
The major advantage in using wireless data traffic system for industrial IoT, are the costs compared to wired solutions. Costs of cables and cable conduits, costs for installation, and the often-underestimated costs of troubleshooting a wired infrastructure. With easier installation and troubleshooting, high security, battery life of up to 7 to 10 years and an increasingly lower prices for wireless sensors, the argument for wireless are many and strong.
Why LoRa and LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN is a communication protocol for compressed data packages, excellent for telemetry and sensor values. It provides low power consumption, long operating ranges and limited need for bandwidth. None of the options, e.g. Zigbee, BlueTooth and Wi-Fi are as strong in all of these wanted characteristics. SigFox, similar to LoRaWAN, requires all data traffic to be stored in the network provider’s own server solutions before further distribution. This results in more variable costs and additional technical dependencies. In your own private LoRa-network you will have full control over the entire communication chain, 24/7.
In addition to great technical performance, LoRa-WAN is a completely open and free standards. Many other communication protocols for industrial- and building automation have license costs or are proprietary locked to a specific manufacturer of sensors and hardware.

LoRa + Connectitude = Industriell IoT?
Among our Connectitude industrial IoT Platform ™ customers, we see a rapidly increasing demand for LoRa solutions in all industries. From simpler need of additional sensors for temperature and humidity to more complex and complete solutions for measurement and control functions. Devices that communicate with LoRa can send data directly to gateways with our platform’s local edge software. Advanced LoRa devices can also receive information from the platform, such as firmware updates or other configurations.
LoRa a good connection alternative for industrial IoT
LoRa is an abbreviation of Long Range. The specified range for LoRa is 151 dB, which means about 10-15 kilometers in urban environment under good conditions. Most of our installations are indoors, in office buildings and factory premises. There, the effective range can vary from a few hundred meters and upwards, depending on the building design and its construction materials.
Should we wait for public city networks for LoRa?
City networks are suitable for intercepting data from sensors etc., spread on large areas and in environments where it is difficult to install your own gateways. For a fully autonomous sensor, which sends its value per hour, for example and in the public waste bin, this is a near-ideal solution. The disadvantage of urban networks is that they are built up as the Sigfox solution, as above. All data traffic must go through the city network’s own server, acting as a message broker. Through a controlled interface for data communication, so-called API, various software then can retrieve their preferred data through sets of predefined queries.
Why should we have our own private LoRa-network?
We are happy to help our customers to develop system integrations for city networks. However, where it is possible to use dedicated and locally installed gateway, we recommend that LoRa devices communicate directly with the Connectitude industrial IoT Platform. It reduces the number of technical dependencies as well as additional costs for services and data traffic. It also provides increased control and flexibility for the entire system solution. The signal chain has less time delay and data can also be sent more often. In a private LoRa network, our platform can handle high samples frequencies, as per second. It is usually the power supply for the sensor that sets the limits.
So is it all Plug-and-Play then?
The reason why the LoRaWAN protocol is just so power-efficient and has so few transmission errors, is that data packages are sent in a very compact and hexadecimal string format. The string format itself is completely standardized by the LoRa Alliance®. However, there are still no strict rules for how the actual information in the strings, the payload, should be structured.
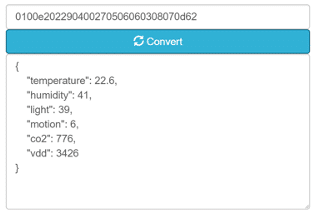
The example above contains a 32-character hexadecimal string, used in a multi-sensor. It represents values for 6 different parameters, presented in a certain order. Some values are integers, others have decimals. Another sensor may have a similar string, but specify values for completely different parameters, or just in a different order. This means that a new type of sensor may need a unique script for translating the data string into the correct values and measurement units. Contact us about which LoRa devices already are compatible.
How safe is a private LoRa network?
LoRa signals are transmitted in on the open and license-free radio frequencies. 433 MHz and 866 MHz in Europe, 915 MHz in Australia and North America, 923 MHz in Asia. The communication between the transmitter and the Connectitude IIoT platform ™ has high security through various forms of mandatory authentication routines. A good quality LoRa device can handle two unique security keys, one Network session key and one Application session key. These keys can be generated by the platform and are then transmitted to the LoRa device via an app requiring near-field communication, NFC. The information must be sent in the same close proximity to the sensor as for contactless payments. Moreover, each unit has its unique ID and a hexadecimal payload that needs decoding, see above. This makes it very difficult to eavesdrop or manipulate the transmissions of data in a private LoRa network.
Do you want to get started with LoRa or have questions about industrial IoT? Please contact Us!